Detecting Diethylene Glycol and Ethylene Glycol Contamination with HPTLC: A Practical Overview
Public health concerns over contaminated liquid drug products have intensified in recent years, especially after multiple poisoning incidents linked to diethylene glycol (DEG) and ethylene glycol (EG) were reported across several countries in 2022 and 2023. These two industrial solvents, when accidentally present in pharmaceutical excipients such as glycerol or propylene glycol, can cause severe toxicity even at low concentrations.
In response, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued guidance in 2023 urging pharmaceutical manufacturers and suppliers to strengthen their quality-control testing. The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) also established a strict safety limit, requiring that DEG and EG levels in excipients must not exceed 0.10% during identity testing.
To support the industry in meeting these requirements, an optimized High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography (HPTLC) method has been developed. Adapted from an earlier TLC approach, this method improves sensitivity and reproducibility, making it a practical tool for routine DEG/EG screening.
Why HPTLC for DEG/EG detection?
✔️ Visual + densitometric detection
✔️ Reliable identification + quantification
✔️ Detect DEG/EG down to 𝟬.𝟬𝟯%
Designed for pharmaceutical QC, R&D, and regulatory labs
A Practical HPTLC Approach for Detecting DEG and EG in Syrup Formulations
The presence of diethylene glycol and ethylene glycol in syrup based pharmaceutical products has raised serious public health concerns in recent years. As a result, reliable and accessible analytical methods are essential for routine screening and quality control. High performance thin layer chromatography offers a practical solution and strong analytical performance.
In this method, syrup samples are prepared using a simple extraction procedure designed to ensure efficient recovery of the target compounds. One gram of syrup is dissolved in methanol and subjected to vortex mixing and sonication to promote complete dissolution. The solution is then centrifuged to remove insoluble components, and the clear supernatant is used for chromatographic analysis.
To support quantitative evaluation, reference solutions of diethylene glycol and ethylene glycol are prepared alongside the samples. A series of concentrations ranging from 0.025 to 0.100 mg per mL is used, providing a reliable calibration range for comparison and measurement.
Chromatographic separation is carried out on HPTLC silica gel plates using an automated sample applicator to ensure precision and reproducibility. Both samples and reference solutions are applied as narrow bands with consistent spacing and positioning. Plate development is performed under controlled humidity and chamber saturation conditions, using a mobile phase composed of acetone, ammonia solution, toluene, and water. The development distance is carefully controlled to achieve effective separation of the analytes.
Following chromatographic development, the plates undergo chemical derivatization using a potassium permanganate based reagent. This step enhances visualization and improves detection sensitivity. After derivatization, the plates are dried and allowed to stabilize before documentation.
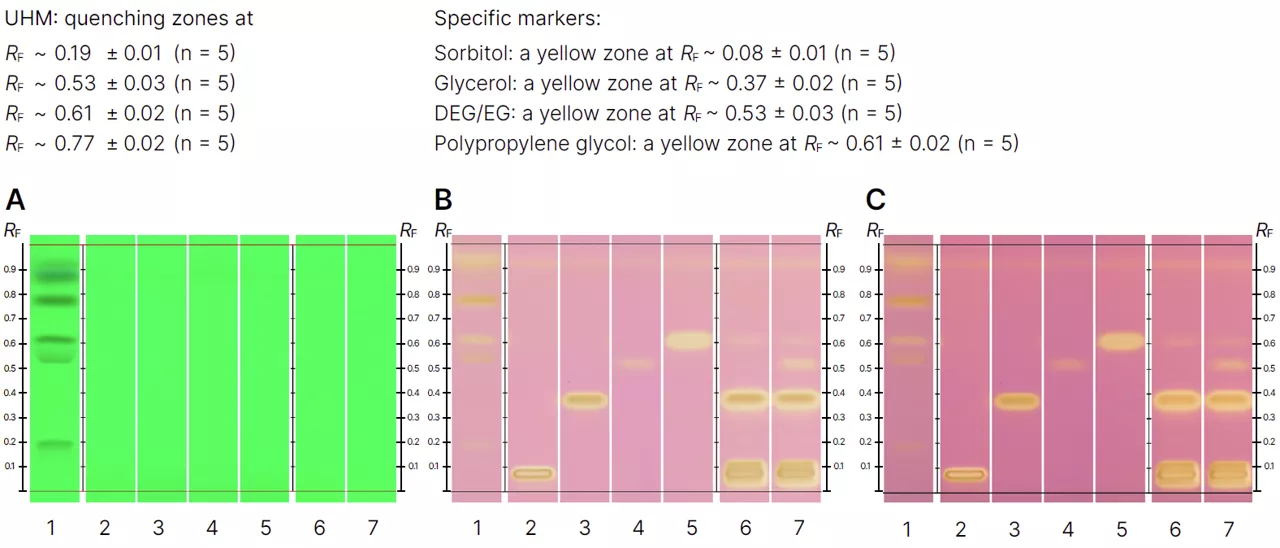
The analytical results are documented using multiple detection modes. Plates are first imaged under ultraviolet light prior to derivatization, then under white light reflection and combined reflection and transmission modes after derivatization. This multi mode documentation ensures clear visualization of both the chromatographic separation and the derivatized zones.
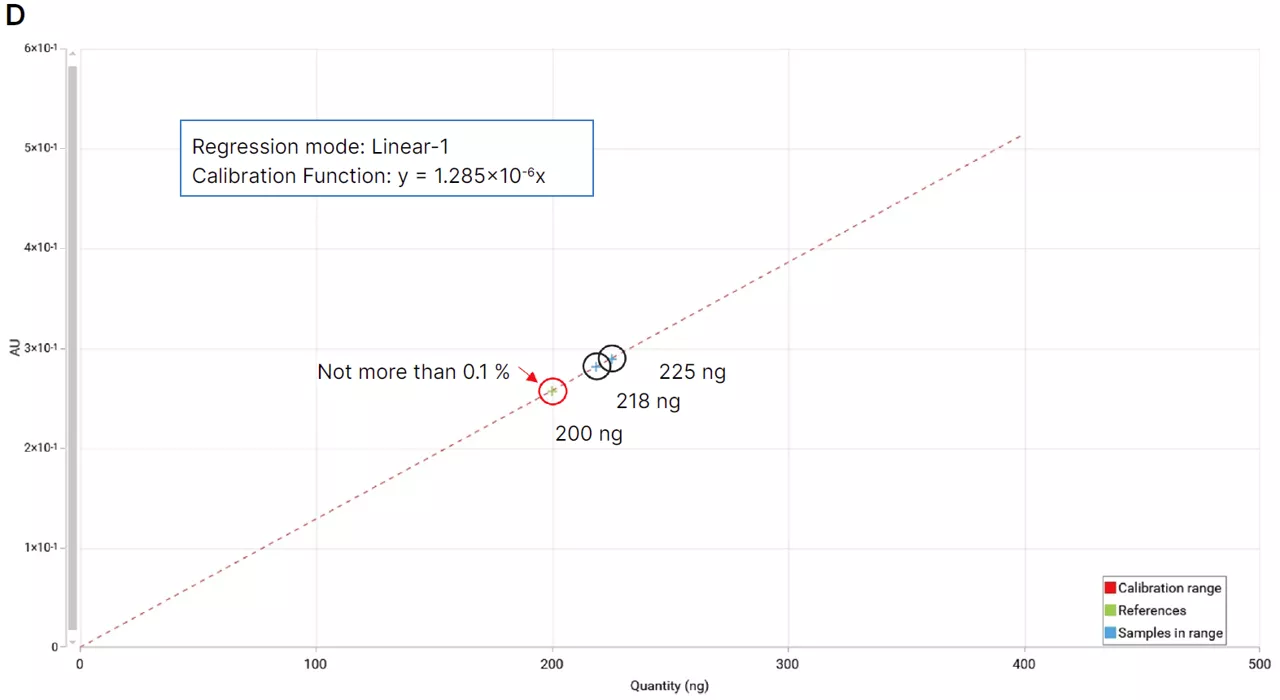
Quantitative analysis is performed using scanning densitometry at a wavelength of 520 nm. The resulting peak profiles are processed using dedicated chromatography software, allowing accurate and reproducible quantification of diethylene glycol and ethylene glycol in syrup samples.
Overall, this HPTLC method provides a reliable and efficient approach for the detection and quantification of diethylene glycol and ethylene glycol in syrup formulations. By combining straightforward sample preparation with automated chromatography and densitometric analysis, the method is well suited for routine quality control and regulatory monitoring, particularly in settings where rapid and cost effective screening is required.





